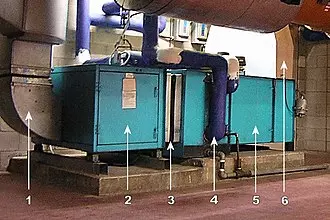
An air handling unit; air flow is from the right to left in this case. Some AHU components shown are 1 - Supply duct 2 - Fan compartment 3 - Vibration isolator ('flex joint') 4 - Heating and/or cooling coil 5 - Filter compartment 6 - Mixed (recirculated + outside) air duct
An air handler, or air handling unit (AHU), is an essential component of a heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. It serves the crucial purpose of regulating and circulating air to maintain comfort and air quality within buildings. From large-scale units to smaller, local terminal units, air handlers play a vital role in creating a pleasant indoor environment for everyone.
Construction
The construction of an air handler revolves around a sturdy framing system with metal infill panels. These panels are designed based on the configuration of the components. In simpler cases, the frame may be made from metal channels or sections with single-skin metal infill panels. For outdoor units, additional weatherproofing measures are taken, including the provision of a weatherproof lid and sealing around joints.
For larger air handlers, a square section steel framing system with double-skinned and insulated infill panels is utilized. This construction not only reduces heat loss or gain but also provides acoustic attenuation. These larger units are often manufactured in a sectional manner, with steel section base rails providing strength and rigidity.
Types of Air Handling Units
Air handling units can be classified based on six key factors:
- Application (the usage of air handling units)
- Air flow control (CAV or VAV air handlers)
- Zone control (single zone or multi-zone air handlers)
- Fan location (draw-through or blow-through)
- Direction of outlet air flow (front, up, or down)
- Package model (horizontal or vertical)
While various methods are used to categorize air handling units, the most common approach is to classify them based on their applications. Companies often advertise their products by highlighting the specific applications they serve, such as normal, hygienic, or ceiling mounted.
Components of an Air Handler
Air handlers consist of several major components, each playing a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and comfort. Some of these components include:
Filters

A RTU viewed from inside with supply diffusers and return vent (center right)
Air filtration is an integral part of air handlers to provide clean and dust-free air to building occupants. Various techniques are employed, including low-MERV pleated media, HEPA filters, electrostatic filters, or a combination of these methods. Gas-phase and ultraviolet air treatments may also be utilized for enhanced air quality.
Hot and Cold Elements
Air handlers are responsible for delivering hot or cold air, or both, to achieve the desired supply air temperature and humidity level. Heat exchanger coils within the air handling unit are used to provide the necessary heating or cooling effect. These coils can be either direct or indirect, depending on the medium used for heating or cooling.
Humidifier
In colder climates, continuous heating can make the air drier, leading to uncomfortable air quality and increased static electricity. To address this, air handlers are equipped with various types of humidifiers, including evaporative, vaporizer, spray mist, ultrasonic, and wetted medium humidifiers.
Mixing Chamber
Maintaining indoor air quality is essential, which is why air handlers incorporate provisions for introducing outside air and exhausting air from the building. By mixing the right amount of cooler outside air with warmer return air, the desired supply air temperature can be achieved. A mixing chamber with dampers is used to control the ratio of return, outside, and exhaust air.
Blower/Fan
Air handlers typically employ a large squirrel cage blower driven by an AC induction electric motor to circulate the air. The fan's speed can be adjusted using inlet vanes, outlet dampers, or variable-frequency drives for precise control. In large commercial units, multiple blowers are used in conjunction with supply and return fans for efficient air movement.
Vibration Isolators and Sound Attenuators
To minimize noise and vibration transmission, air handlers are equipped with vibration isolators and sound attenuators. Vibration isolators, typically made of rubberized canvas-like material, absorb the motion generated by the blowers and prevent it from reaching the attached ducts. Sound attenuators, on the other hand, reduce noise before the ductwork enters noise-sensitive areas.
The Leading Manufacturers
Numerous reputable manufacturers produce high-quality air handling units. Some of the major players in the market include:
- AAON
- Carrier Corporation (Bryant and Payne brands included)
- CIAT Group
- Daikin Industries (McQuay International, Goodman, and Airfel brands included)
- Johnson Controls (York International brand included)
- Lennox International
- Rheem (Ruud brand included)
- Trane
- Vertiv
With their expertise and experience, these manufacturers contribute to the development and advancement of air handling technology.
Discovering Comfort and Air Quality
Air handlers are the unsung heroes behind comfortable indoor environments and improved air quality. By efficiently regulating air flow, controlling temperature and humidity, and ensuring proper air filtration, they contribute significantly to the well-being of individuals within buildings. The marvels of air handlers continue to provide a breath of fresh air in our everyday lives.









