How to Calculate Loan-to-Value Ratio?
The loan-to-value ratio (LTV) is a crucial measure of risk in the commercial real estate market. It compares the size of a loan to the appraised value of the property securing the financing. Financial institutions use it to analyze credit risk when evaluating mortgage applications. The LTV ratio is determined by the amount of debt provided by the lender and the appraised value of the property.
What is a Good Loan-to-Value Ratio?
A "good" loan-to-value ratio (LTV) in the commercial real estate market is typically around 70% to 80%. However, economic conditions and market demand fluctuations can cause this range to fluctuate. Risk-averse lenders often set a maximum LTV ratio of around 75% to limit their lending portfolio's risk.
 Loan-to-Value Calculator (LTV)
Loan-to-Value Calculator (LTV)
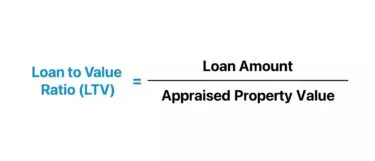
Loan-to-Value Ratio Formula
The LTV ratio formula divides the loan amount by the appraised property value. The resulting figure is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage.
Loan-to-Value Ratio Calculation Example
Let's say a commercial real estate investor obtained a $525,000 mortgage loan to purchase an $875,000 office building. The LTV ratio would be 60.0%. It means the lender is providing 60.0% of the property's market value, while the investor contributes 40.0% as an equity investment.
How to Interpret LTV Ratio in Real Estate Lending?
Higher loan-to-value (LTV) ratios are generally seen as riskier financing arrangements. Lenders prefer lower LTV ratios because they indicate less credit risk and lower interest rates. A higher LTV ratio can lead to higher interest rates, monthly payments, and the need for private mortgage insurance. It can also limit flexibility in refinancing and result in a lower credit score.
LTV Ratio vs. CLTV Ratio: What is the Difference?
The combined loan-to-value (CLTV) ratio measures two mortgages combined against the appraised property value. It takes into account the outstanding loan balance on the first mortgage and the proposed second mortgage. A CLTV ratio of 52% indicates that the total loan amount is 52% of the property's appraised value.
Understanding the loan-to-value ratio is crucial for both lenders and borrowers in the real estate market. It helps assess risk, determine down payments, and negotiate favorable lending terms. By keeping the LTV ratio low, borrowers can benefit in the long run by securing better interest rates and having more options for refinancing.

















