Wall sections are a crucial communication tool between architects and contractors, providing vital information about a building's construction. However, creating accurate and detailed wall sections can be intimidating, especially for architecture students and inexperienced architects.
Understanding Wall Sections: Demystifying the Basics
In simple terms, wall sections are detailed architectural drawings that showcase a vertical cut through a wall. These drawings reveal the various layers and components of a wall, including structural elements, insulation, finishes, and cladding. By studying wall sections, one can gain valuable insights into construction techniques, material specifications, and the relationship between different building components within the wall.
It's important to note the distinction between building sections and wall sections. While building sections provide a holistic view of a building's vertical arrangement, wall sections zoom in on the specifics of wall construction. Both types of sections are essential in architectural drawings, as they offer different perspectives and knowledge.
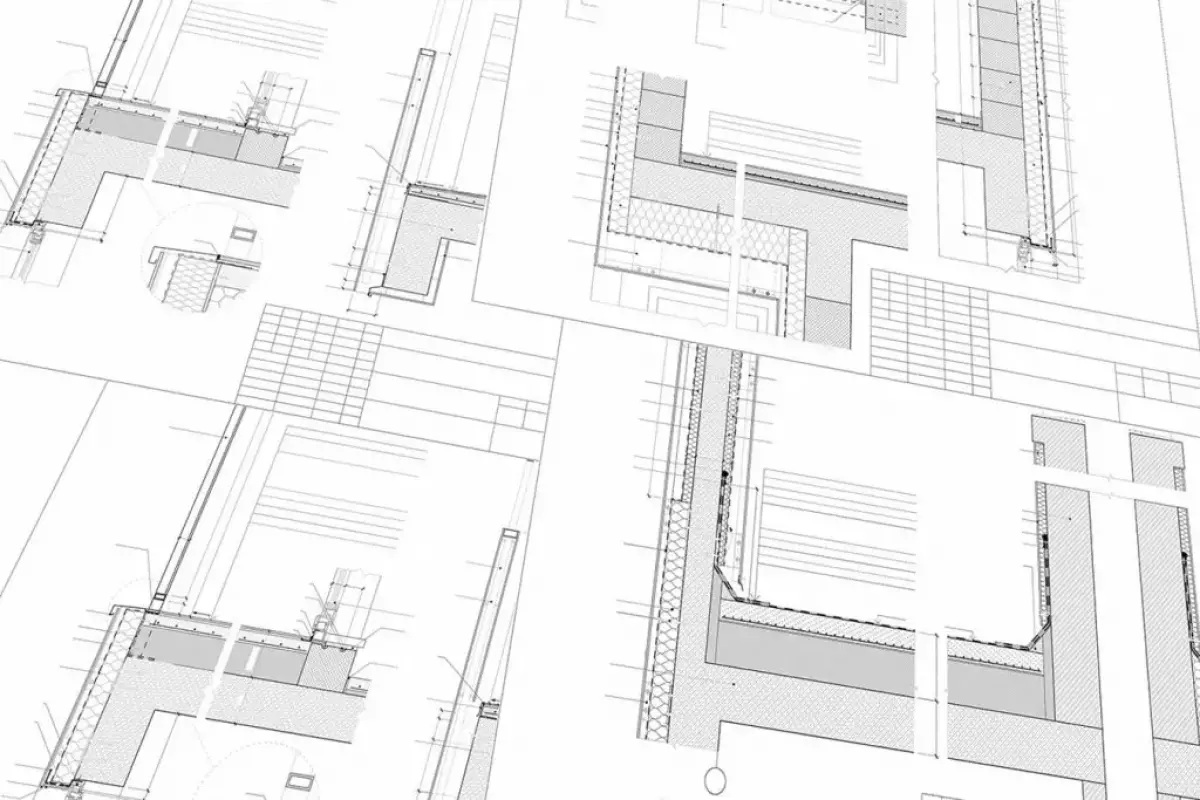 Wall Sections: An Architect's Guide
Wall Sections: An Architect's Guide
Essential Considerations for Wall Section Detailing
When creating wall sections, there are several key elements and factors to consider. Let's explore some of the most important ones:
Bearing vs Non-Bearing Walls
Understanding the distinction between bearing and non-bearing walls is crucial. Structural walls are responsible for carrying the weight and load of the building, while non-structural walls serve as room dividers. The choice between these two types depends on the intended function of the walls and should be carefully considered.
R-Values and Sound Attenuation
An important aspect when designing walls is the insulation's R-value, which measures the heat resistance of materials. Thicker walls with a combination of suitable insulating materials ensure a higher R-value, preventing heat from escaping easily. Additionally, sound attenuation should be taken into account to create acoustically comfortable spaces.
Cladding Materials: Aesthetics and Functionality
Cladding serves as both an aesthetic feature and a protective layer. The choice of cladding materials and the waterproof membrane behind them is essential to ensure the structure remains unaffected by moisture. Different cladding designs, such as horizontal, vertical, and diagonal, offer various aesthetic and functional advantages.
Roof Types: From Flat to Pitched
Roofs play a vital role in a building's functionality and aesthetics. Flat roofs are cost-effective but have a shorter lifespan, while pitched roofs offer durability and allow rainwater runoff. Additional roof types, including warm roofs, cold roofs, and inverted roofs, serve specific functions and warrant careful consideration.
Connecting Windows and Wall Sections
Properly connecting windows to wall sections requires the use of cavity closers and damp-proof courses (DPCs) to prevent water infiltration. The sill of a window acts as protection from moisture, and lintels play a crucial role in supporting the blockwork at the head of a wall opening.
Floor Types: Strength, Durability, and Insulation
Choosing the appropriate flooring material depends on factors such as longevity, strength, fire resistance, and sound resistance. Concrete and timber are commonly used materials for both ground-bearing and suspended concrete floors. Beam and block floor systems provide a sturdy base for leveled layers of material.
Damp-Proof Course (DPC)
To prevent moisture intrusion, a DPC is placed beneath the structure to create a barrier. It is typically made of polyethylene and is positioned above the external ground level. DPCs are essential in maintaining the integrity of the building's structure.
Foundations: Supporting the Structure
Foundations bear the weight of a building and provide essential support. There are four main types of foundations: strip foundation, pile foundation, raft foundation, and pad foundation. Each type is chosen based on factors such as soil conditions and the desired structure.
Drawing an Effective Wall Section
Drawing an effective wall section detail requires attention to detail and adherence to established standards. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Determine the scale: Choose a scale that allows for clear representation of all layers and components.
- Select the specific portion of the wall to be detailed.
- Draw the basic outline, including the floor and ceiling lines.
- Add structural elements, such as studs, joists, or concrete blocks.
- Layer in materials, accurately representing their thickness and texture.
- Detail components and connections, showing how different materials and components interact.
- Include annotations, labeling each material and component and adding relevant notes.
- Represent doors and windows if applicable, detailing frames, glazing, and other relevant details.
- Add key dimensions, such as overall wall thickness and the thickness of each material layer.
- Review the drawing for accuracy and clarity, ensuring all necessary information for construction is conveyed.
Creating an effective wall section requires a combination of technical knowledge and attention to detail. By following these steps, architects can effectively communicate a building's structure and construction methods.
In Conclusion
Mastering the art of wall sections is crucial for effective architectural communication. By following building regulations, considering essential factors like foundation types, cladding materials, and insulation, architects can create sustainable and visually appealing structures.
Remember, while plans can be altered, adherence to technical recommendations is vital to avoid any unforeseen issues. With careful consideration and attention to detail, architects can create accurate and informative wall sections that facilitate successful construction projects.

















