Real estate investors are always on the lookout for strategies that can help them grow their portfolios and increase net worth more efficiently. One common tax strategy that savvy investors often turn to is the 1031 Exchange. In this article, we'll take you through the six steps to understanding the 1031 Exchange rules, so you can take advantage of this powerful tool to boost your real estate investments.
Step 1: Understand the IRS Definition
The first step in mastering the 1031 Exchange rules is to understand how the IRS defines it. Under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code, a like-kind exchange refers to the exchange of real property used for business or held as an investment solely for other business or investment property of the same type. This strategy has been in place since 1921 to encourage active reinvestment and avoid taxation of ongoing property investments.
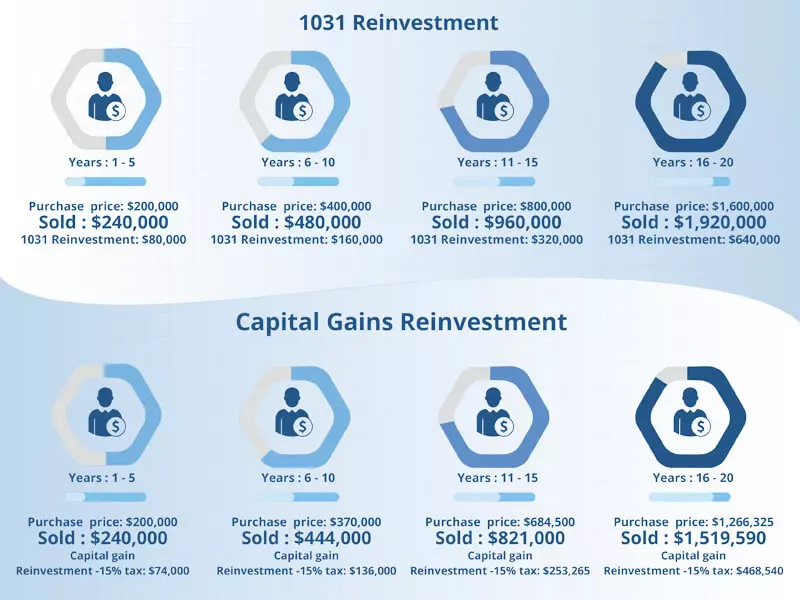 Image: 1031 exchange rules from IRS
Image: 1031 exchange rules from IRS
Step 2: Identify Eligible Properties
To successfully execute a 1031 Exchange, it's crucial to identify eligible properties. According to the IRS, properties are considered like-kind if they have the same nature or character as the one being replaced, regardless of their quality or level of improvement. Real estate investors can exchange properties such as small apartment buildings for larger apartment projects, office buildings, or vacant land.
Step 3: Review the Five Common Types of 1031 Exchanges
There are five common types of 1031 exchanges that real estate investors often use:
- Delayed exchange: The sale of one property and the subsequent purchase of a replacement property within the allowed timeframe.
- Delayed/simultaneous exchange: The simultaneous purchase of the replacement property while selling the current property.
- Delayed reverse exchange: The purchase of the replacement property before selling the current property.
- Delayed build-to-suit exchange: The replacement property is built according to the investor's specifications.
- Delayed/simultaneous build-to-suit exchange: The purchase of a built-to-suit property before selling the current property.
It's important to note that during the identification and purchase process, the investor cannot receive the proceeds from the sale of the property. The funds are held in escrow by a qualified intermediary until the replacement property is acquired.
Step 4: Follow the Three Important 1031 Exchange Rules
To ensure a successful 1031 exchange, it's crucial to follow three important rules:
- The replacement property must be of equal or greater value than the one being sold.
- The replacement property must be identified within 45 days from the sale of the current property.
- The purchase of the replacement property must be completed within 180 days from the sale.
 Image: 1031 exchanges rules and time limits
Image: 1031 exchanges rules and time limits
Step 5: Explore How a 1031 Exchange Works in the Real World
Let's take a look at a real-world example to understand how a 1031 exchange works. Consider a multifamily building with a cost basis of $1 million and a market value of $2 million. Without using a 1031 exchange, a real estate investor would be liable for capital gains tax on the $1 million profit. However, by utilizing a 1031 exchange, the investor can defer paying capital gains tax by reinvesting the proceeds in a like-kind replacement property.
Step 6: Work to Eliminate Capital Gains Tax Permanently
One of the main benefits of utilizing a 1031 exchange is the deferral of capital gains tax. However, when the investor passes away, the property can be passed on to an heir, and any deferred capital gains taxes are eliminated through stepped-up basis valuation. This means that with proper estate planning, investors can completely eliminate the capital gains tax on their real estate investments.
In Conclusion: Remember the Power of 1031 Exchanges
1031 exchanges provide real estate investors with an opportunity to defer paying capital gains tax and reinvest the proceeds in like-kind replacement properties. By understanding the rules and following the guidelines, investors can maximize their investment potential and enjoy higher rental income while growing their real estate portfolios. Take advantage of the 1031 exchange strategy and unlock the full potential of your investments!
 Image: 6 quick facts about 1031 exchanges
Image: 6 quick facts about 1031 exchanges

















